Online Learning Center
An online educational resource will be established to help build climate change literacy throughout Maryland communities. A library of course modules is being developed with more content being published over the next few weeks (in the first quarter of 2023). Read below for descriptions of recorded primer education workshops and micro-literacy modules that will be posted on this resource. Active links below denote recordings already available.
Primer Education
Climate Change Ambassador Training Series
This series was developed to organizations to leverage as a means to building consistent literacy and understanding of climate change science, projections and implications across their workforces. The program has been developed with a beginner level (Tier 1) and an successor module (Tier 2).
Tier 1
This 4-part series is broadly applicable to a wide-range of roles and levels of seniority/leadership.
Climate Impacts and Implications in the Mid-Atlantic & Maryland
Climate Policy from Global to Local and How Maryland Is Responding
Learning Objectives
The fundamentals of climate change science and overview of climate impacts on infrastructure, public health, local government operations, disaster preparedness/emergency response, and economic vitality.
The impacts of climate change in the Mid-Atlantic and Maryland, including sea level rise, flooding, extreme weather events, and temperature and precipitation changes. The implications of these impacts on the built and
natural environments as well as for public health, safety, and well-being. The disproportionate impacts of climate change on frontline communities and vulnerable populations.Principles of greenhouse gas (GHG) accounting, the energy, water, food and waste nexus, and reducing GHG footprints.
Understanding the climate change policy context from international, to national and local levels.
Tier 2
This 3-part series is upon Tier 1 and adds content intended for more senior leadership and personnel with governance, supervisory and planning responsibilities that intersect with climate change.
Learning Objectives
The fundamentals of climate vulnerability and risk assessment as well as related decision-support resources.
The business case for Enterprise Risk Management (ERM), including evaluating economic and budget implications of climate change, prioritizing risk, and managing risk within an ecological, social, and governance (ESG) framework.
How to engage in ERM with a climate lens, including governance for effective risk management, risk identification, prioritization, and management; tools and skills needed; gathering data and other input; maturing goals; and benchmarking.
Building organizational capacity for a climate transition, including building culture and capacity for change and success, innovation and entrepreneurship in government, establishing climate-related performance objectives and job qualifications, working across organizational boundaries, and outreach to and engaging with stakeholders and external stakeholders to plan and implement effective climate action.
Micro-literacy Modules
The following micro-literacy modules (generally between 8 and 14 minutes in length) will be published in the coming weeks.
Climate Change: Just the Facts
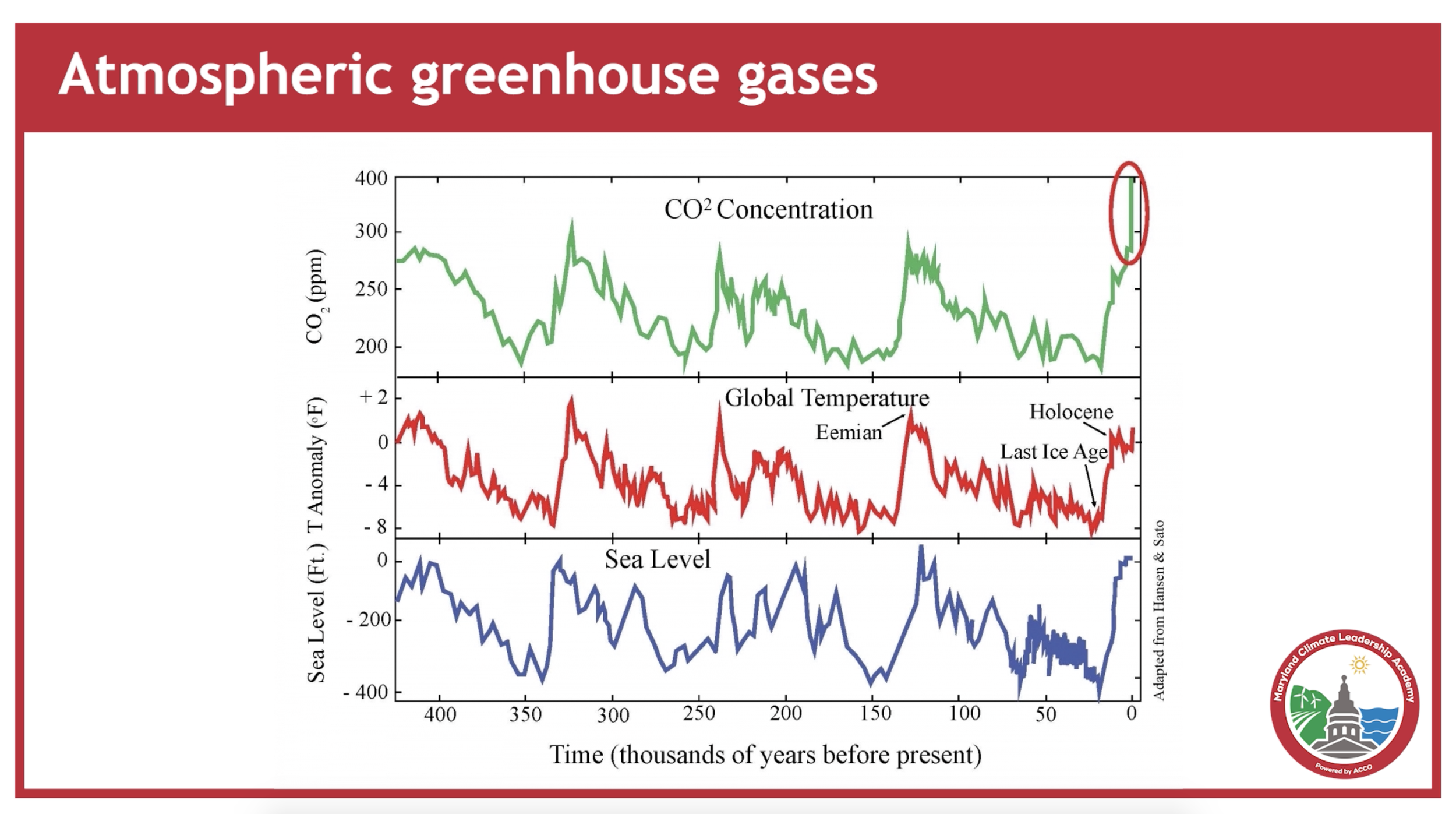
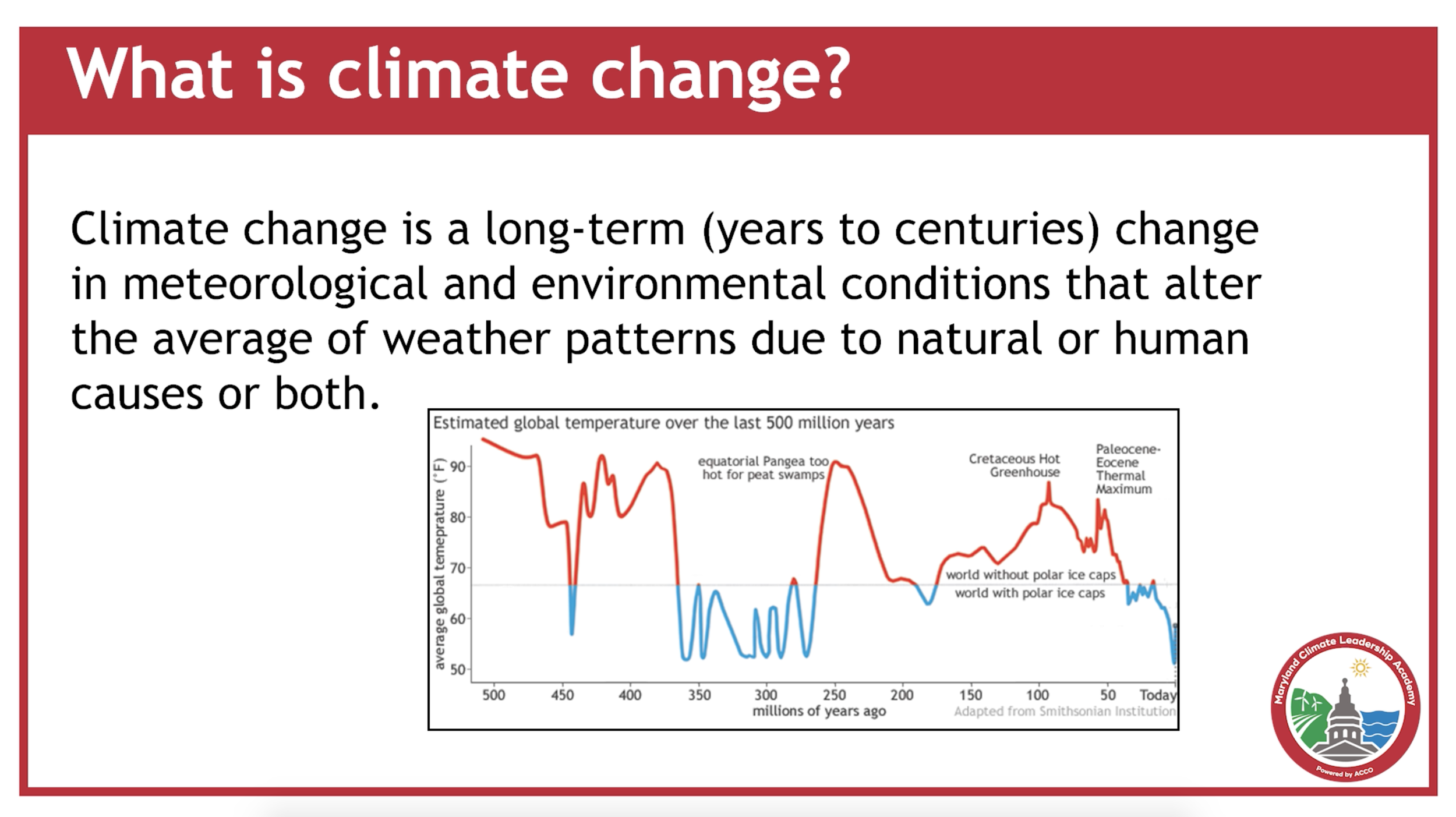
The climate is changing and increasingly disrupting our daily lives in Maryland. While climate has changed many times throughout Earth’s long history, the current rate of rise in global temperature is unprecedented and carries a human fingerprint. Maryland is feeling the impacts now, and these impacts are expected to increase in the future, affecting our neighborhoods, health, economy, food and natural resources, and our children’s future.
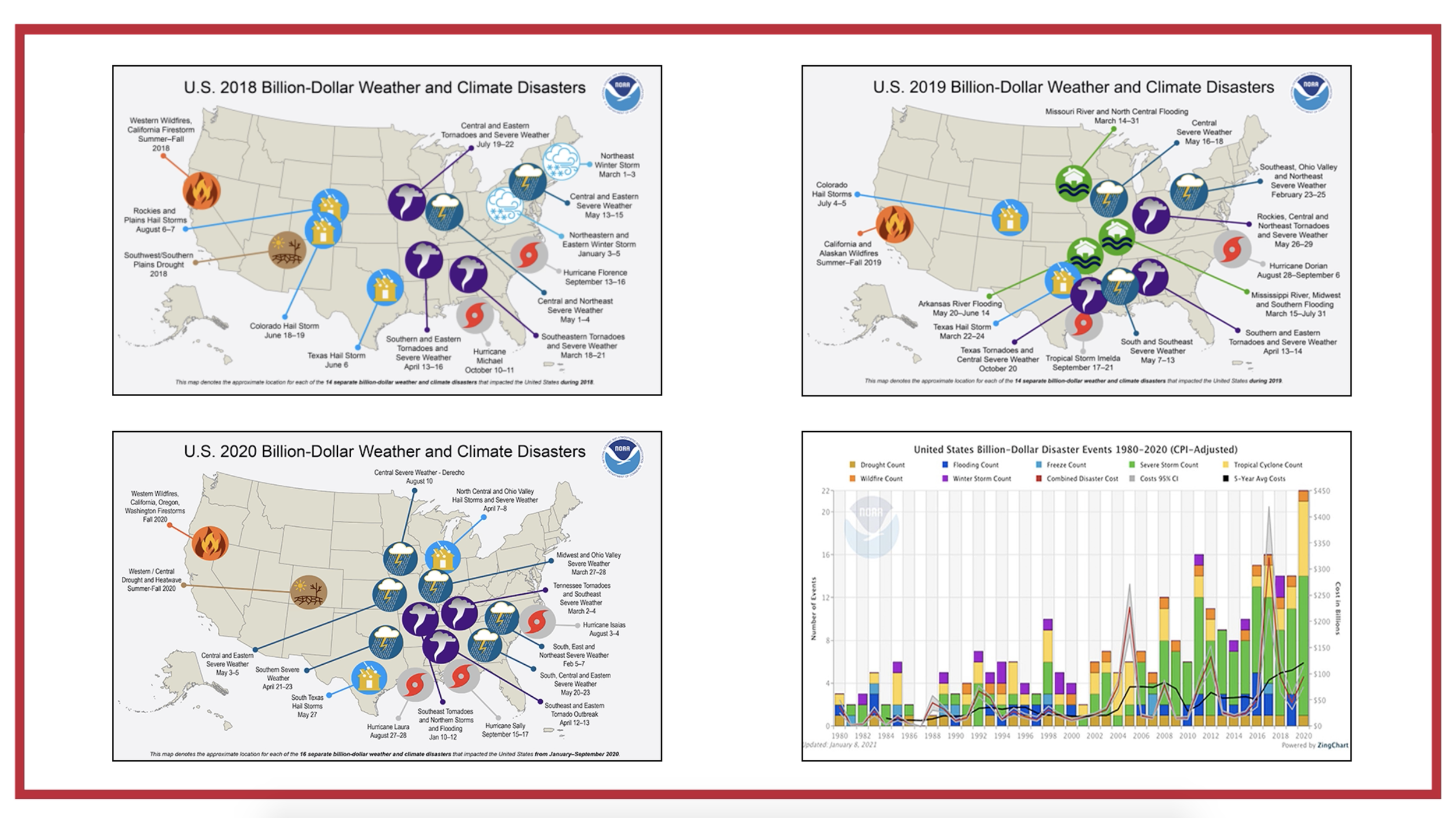
Screenshots from the Module
What's the Difference between Weather & Climate
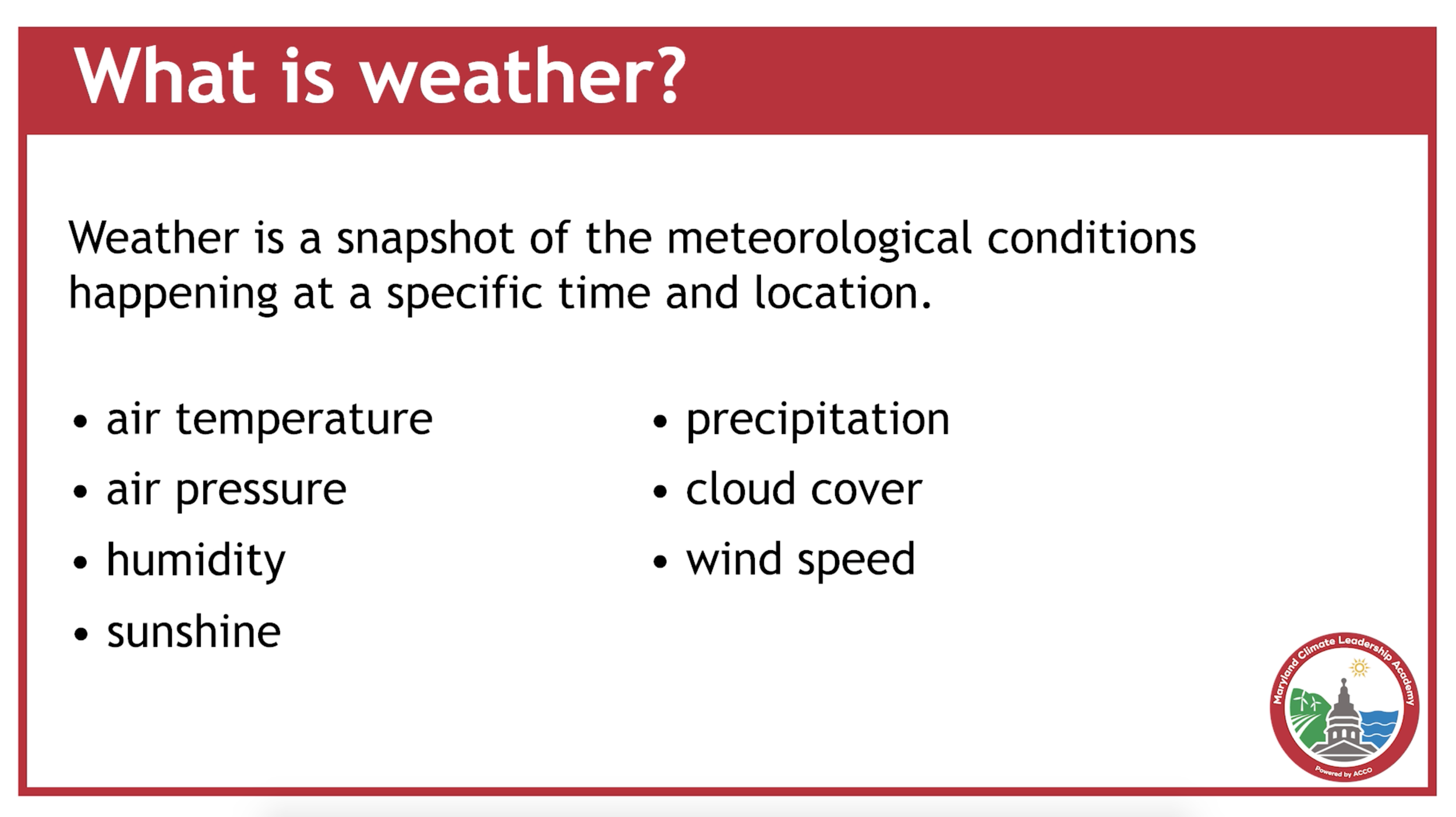
What’s the difference between climate and weather? What’s the difference between climate variability and extreme weather events? We frequently hear these terms in news reports and weather forecasts. This video clarifies the differences so we can better understand how our families, communities, and state will be affected by changing weather and climate. Many Maryland residents have already experienced intense storms, flooding, extreme heat, and prolonged drought. We expect these extreme events to increase in frequency and/or intensity in the future. These weather extremes impact daily life in Maryland in many ways. Learn where you can find out more about extreme events and how Maryland is advancing solutions to protect its residents.
Screenshots from the Module
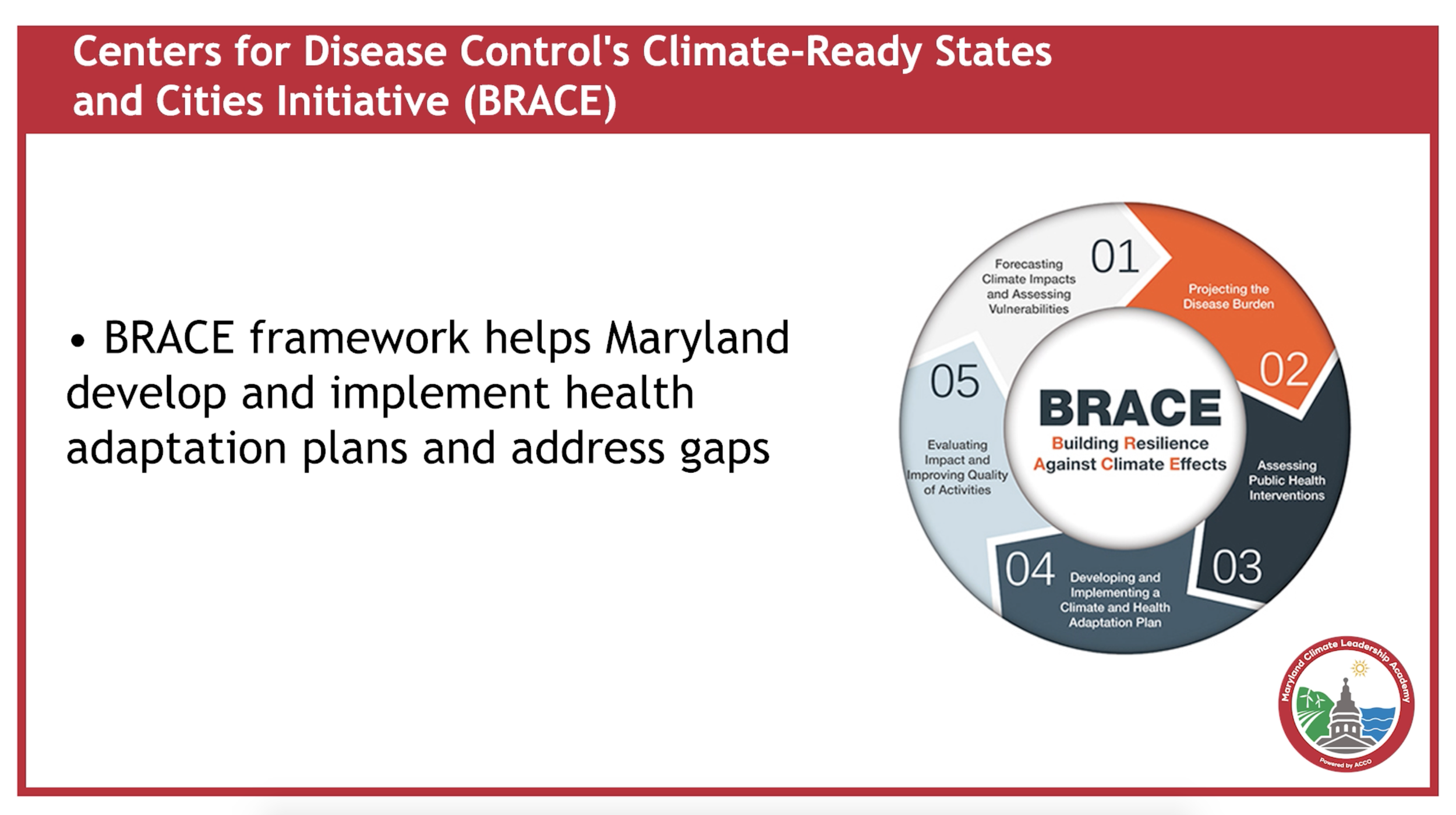
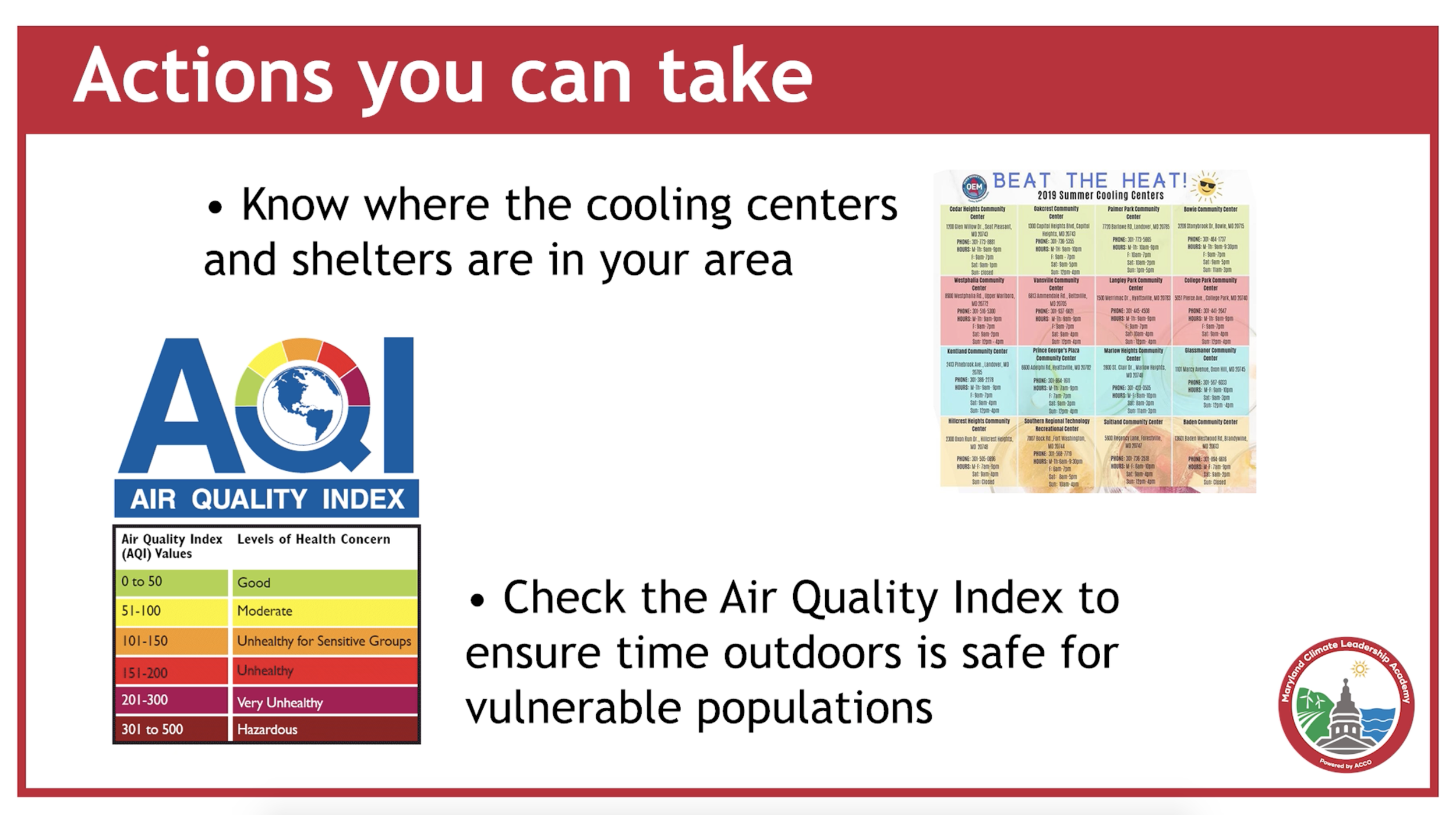
Keeping Healthy in a Changing Climate
Accelerated climate change affects our physical and mental health in ways we’ve never dealt with before. In Maryland, we’ve already experiencing extreme heat and increased storms, flooding, and sea level rise, impacts that affect our health and safety. Extreme heat and flooding events are likely to pose serious public health risks in the coming decades. Air and water quality and food supplies are at risk, with a range of health implications for Marylanders. Fortunately, Maryland has responded and continues to develop policies and programs to protect is citizens and build resilience throughout the state. Learn how Maryland is addressing the public health challenges of climate change and what you can do to protect your family and community from extreme heat and flooding events.
Screenshots from the Module
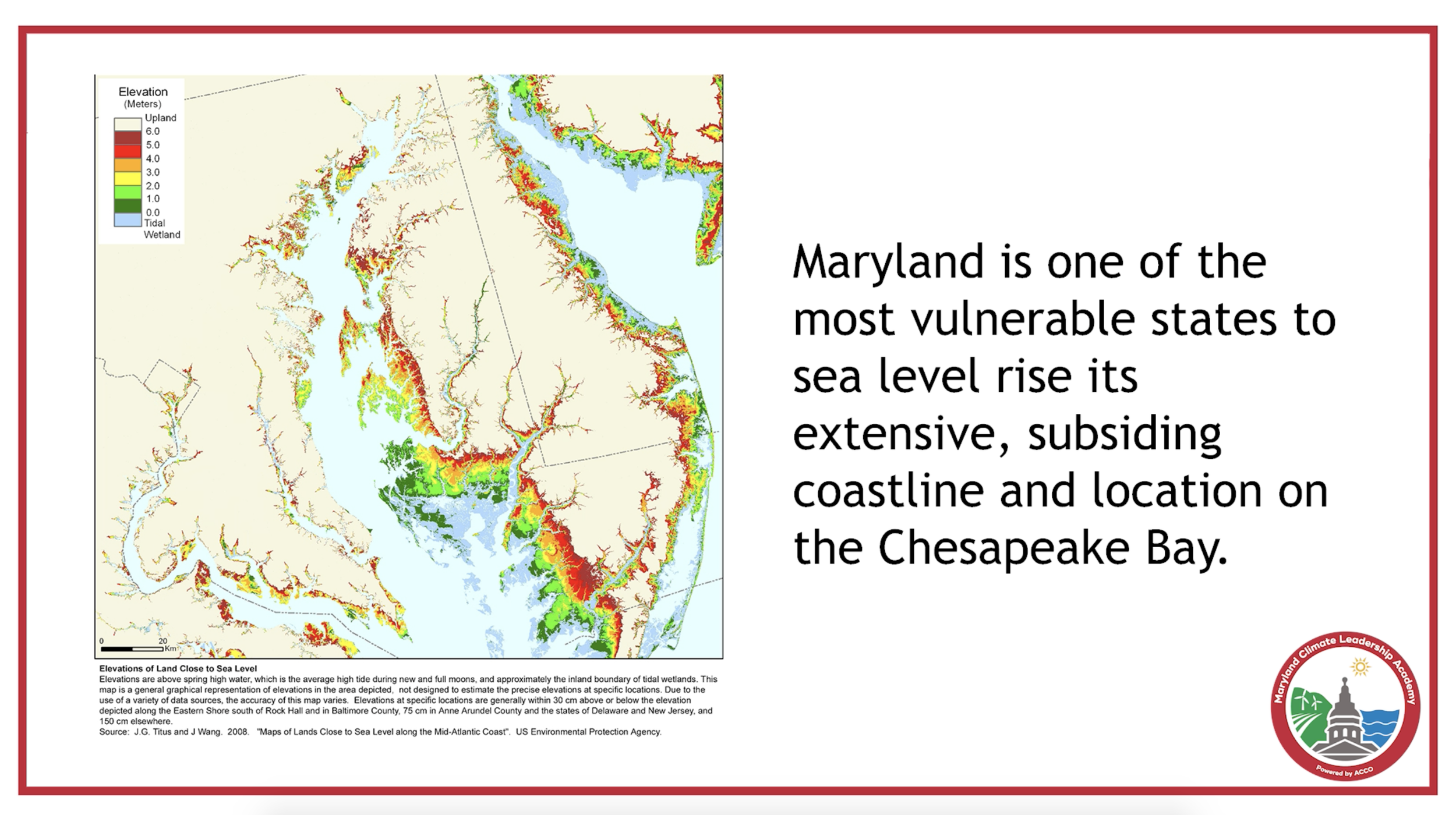
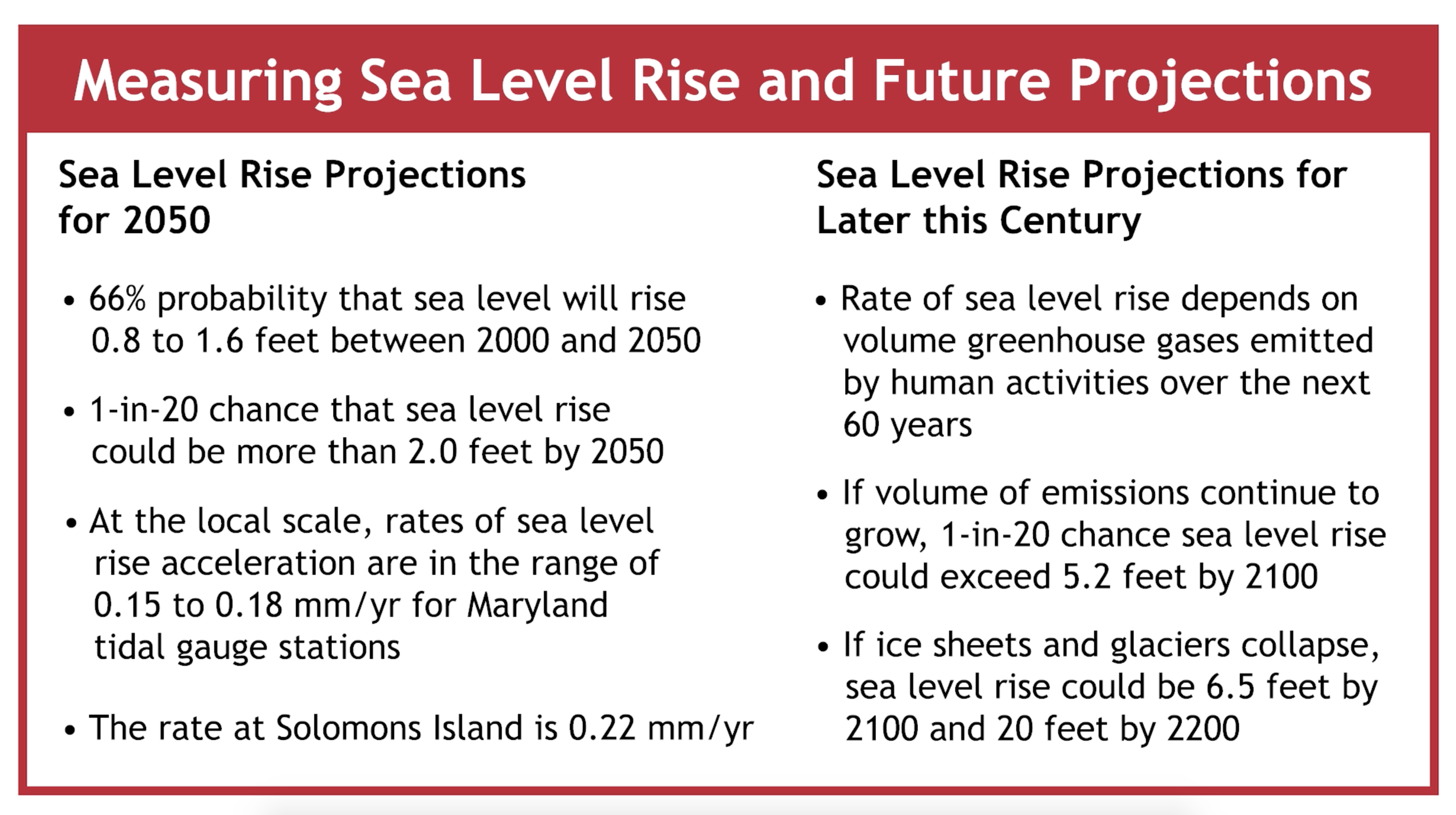
Oceans, Coasts and the Chesapeake Bay
Climate change is already altering our oceans, coasts, and the Chesapeake Bay. Maryland is experiencing a relatively rapid rise in sea level, exacerbating coastal inundation and erosion from storms, high-tide flooding, saltwater intrusion, and changing environmental conditions along the coast and in the Chesapeake Bay. This video highlights what climate change impacts are already happening and what we expect in the future based on new statewide sea level rise projections produced by the Maryland Commission on Climate Change. Future impacts on coastal communities and ecosystems, the fishing economy, and tourism are also presented. In response, Maryland is helping coastal communities become more resilient by reducing losses and adapting to changing conditions.
Screenshots from the Module